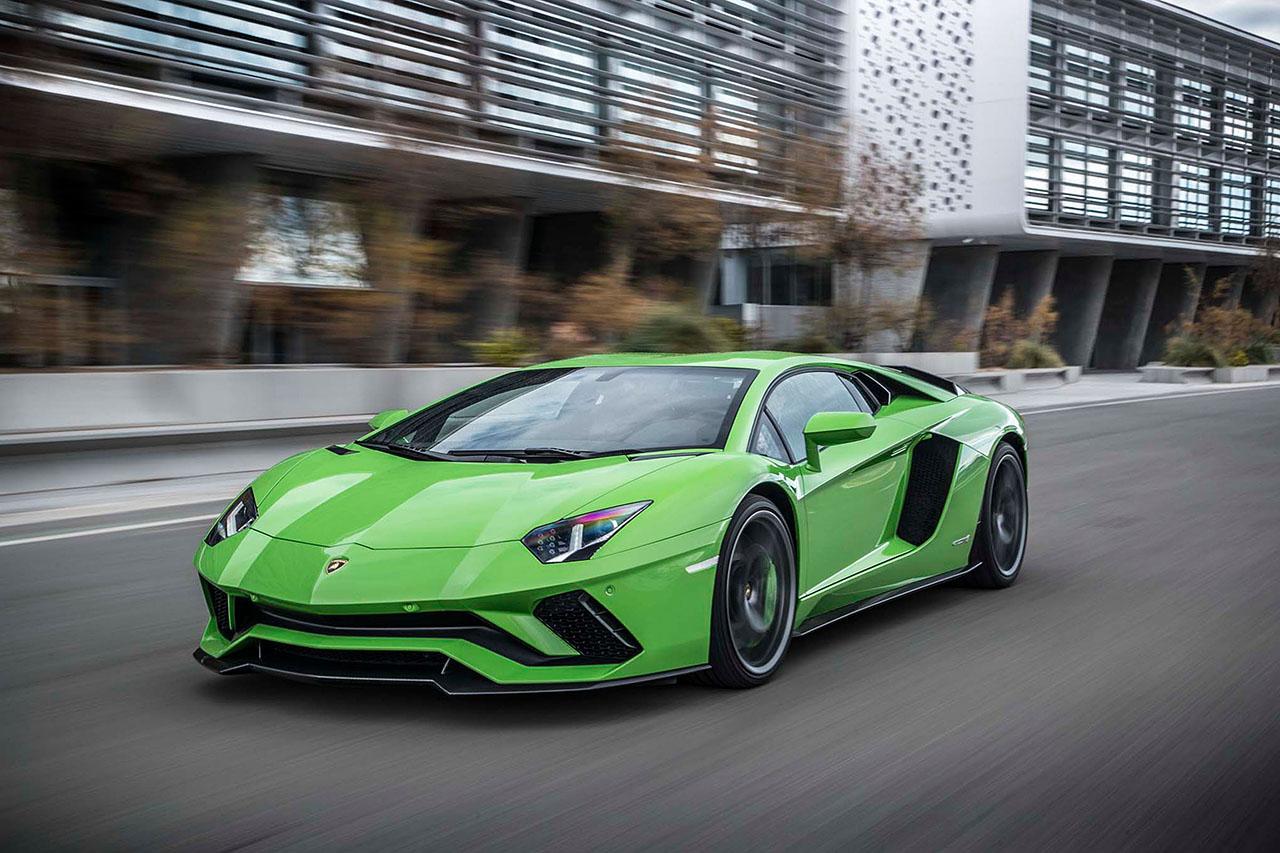
In automotive engineering, the engine is the heart of every vehicle. This article delves deep into these engine types, emphasizing naturally aspirated engines, particularly in the context of Lamborghini, a marque synonymous with high-performance cars.
Different Types of Engines
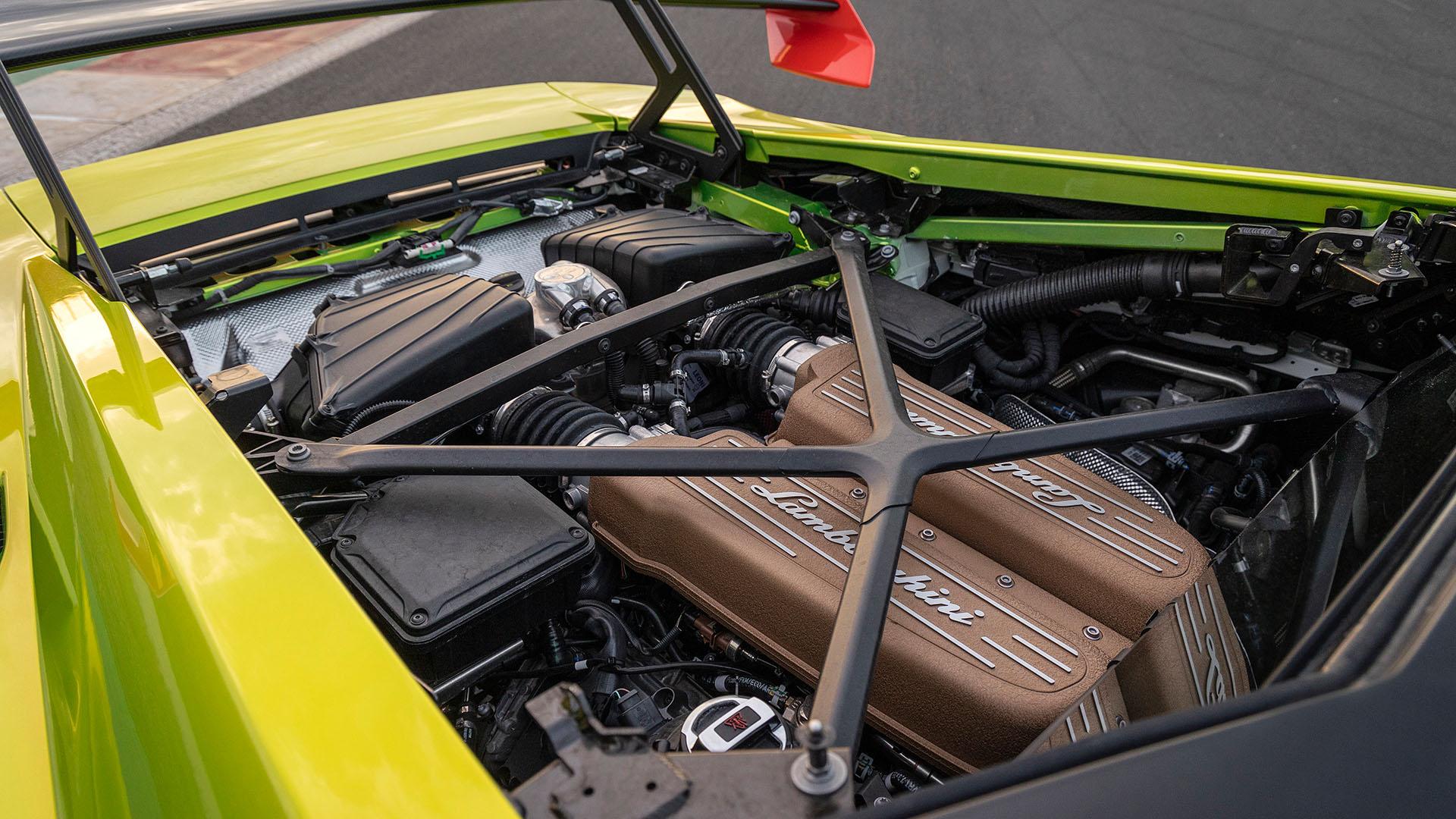

1. Naturally Aspirated Engines
Naturally aspirated engines represent the most traditional form of internal combustion engines. They function without the assistance of any forced induction system, relying entirely on atmospheric pressure to draw air into the combustion chambers. The air mixes with fuel, and the resulting mixture is ignited to create the power stroke that drives the engine. The absence of forced induction systems such as turbochargers or superchargers simplifies the engine’s design, reducing potential maintenance issues and providing a more linear and predictable power output. These engines are favored for their direct throttle response and the purity of their sound, which is unaltered by the whine or whistle of turbochargers or superchargers.
2. Turbocharged Engines
Turbocharged engines feature a turbine driven by exhaust gases to compress air just before it enters the combustion chamber. This compressed air allows more fuel mixture to be burned, significantly increasing the engine’s power and efficiency compared to a simple naturally aspirated engine of the same size. Turbochargers effectively utilize the exhaust gases that would otherwise be wasted to boost the engine’s performance. While they offer improved fuel efficiency and higher power output, turbocharged engines can suffer from “turbo lag” — a delay in response time when the driver accelerates. This lag occurs because the turbocharger needs time to spool to the speed at which it can start compressing air effectively.
3. Supercharged Engines
Supercharged engines, like turbocharged ones, force more air into the combustion chamber to increase power. The critical difference is that superchargers are mechanically driven directly by the engine, typically via a belt attached to the crankshaft. This direct connection eliminates the lag time associated with turbochargers, allowing for instantaneous power delivery. Superchargers are especially effective at low RPMs, significantly increasing low-end torque. However, because the engine powers them, they can be less efficient in fuel consumption than turbochargers.
4. Electric Engines
Electric engines, or motors, represent a significant shift in automotive technology. These engines convert electrical energy into mechanical energy using electromagnetic induction. Electric motors are known for their instant delivery of torque, high efficiency, and quiet operation. They are increasingly popular in the automotive world, especially in the context of environmental sustainability, as they produce no direct emissions.
5. Hybrid Engines
Hybrid engines combine an internal combustion engine (naturally aspirated, turbocharged, or supercharged) with an electric motor. This combination aims to offer the best of both worlds: the extended range and rapid refueling capabilities of conventional engines, with the efficiency and low emissions of electric motors. In a hybrid system, the electric motor can assist the combustion engine, reducing its workload and improving fuel efficiency. Some hybrid systems also allow the car to operate solely on electric power to a small distance.
6. Rotary (Wankel) Engines
Rotary engines, also known as Wankel engines, are a unique type of internal combustion engine. They utilize a triangular rotor that revolves in an epitrochoid chamber instead of the traditional piston and cylinder design. This engine is known for its compact size, smooth operation, and high power-to-weight ratio. However, rotary engines have faced fuel efficiency, emissions, and long-term reliability challenges. Differences Between These Engine Types
Differences Among Engine Types

The most fundamental difference lies in the method of air intake
Air Intake Method
- Naturally Aspirated Engines: Utilize atmospheric pressure for air intake. They have no mechanism to force more air into the combustion chambers.
- Turbocharged Engines: Uses a turbine driven by exhaust gases to compress air into the engine, significantly increasing air intake.
- Supercharged Engines: Compress air into the engine using a mechanically driven compressor, usually a belt connected to the engine.
- Electric Engines: Electric engines do not have an air intake system as they do not rely on internal combustion. They use electrical energy to power a motor.
- Hybrid Engines: Combine the air intake methods of internal combustion engines (naturally aspirated, turbocharged, or supercharged) with an electric motor that requires no air intake.
- Rotary Engines: Rotary engines use a rotating triangular rotor for air intake and combustion, differing significantly from the conventional piston and cylinder method.
Power Delivery
- Naturally Aspirated Engines: Offer a linear and consistent power delivery with no lag in response.
- Turbocharged Engines: Can suffer from “turbo lag,” a delayed response when accelerating, due to the time needed for the turbo to spool up.
- Supercharged Engines: Provide immediate power delivery due to their direct mechanical connection to the engine, eliminating lag.
- Electric Engines: Deliver power instantly due to the nature of electric motors, providing immediate torque from zero RPM.
- Hybrid Engines: Benefit from the instant torque of electric motors while also using the gradual power increase of combustion engines.
- Rotary Engines: Offer smooth and high-revving power delivery but can be less efficient at lower RPMs.
Efficiency and Output
- Naturally Aspirated Engines: Generally less efficient and have a lower power output than forced induction engines of the same size.
- Turbocharged and Supercharged Engines: Increase both efficiency and power output, with turbochargers typically being more fuel-efficient.
- Electric Engines are highly efficient, converting over 90% of electrical energy into mechanical energy, with zero emissions during operation.
- Hybrid Engines: Improve overall efficiency by combining the benefits of electric motors and combustion engines, often leading to lower emissions and even improved fuel economy.
- Rotary Engines: While offering a high power-to-weight ratio, they traditionally lag in fuel efficiency and emissions compared to piston engines
Why People Prefer Naturally Aspirated Engines

Simple Construction
Naturally aspirated engines are characterized by their straightforward design. The absence of complex forced induction systems like turbochargers or superchargers means fewer components can fail. This simplicity often results in a lighter engine, which can benefit the vehicle’s overall weight distribution and handling. This weight advantage can be crucial for achieving better balance and agility in performance cars.
Less Complicated
The fewer parts in a naturally aspirated engine make it more accessible and easier to understand, especially for mechanics and enthusiasts who prefer to do their maintenance and modifications. This simplicity reduces complications during repairs and maintenance, potentially reducing costs and downtime.
Reliability
The straightforward design of naturally aspirated engines often results in more excellent reliability. With fewer components like intercoolers, turbochargers, or superchargers, there are fewer potential points of failure. This reliability is particularly valued in scenarios where dependable performance over long periods is crucial, such as in off-road vehicles or regions where specialized maintenance is not readily available.
Linear Power Delivery
For driving purists and enthusiasts, naturally aspirated engines’ linear and predictable power delivery is highly prized. Unlike turbocharged engines, which can have a delayed response, naturally aspirated engines provide immediate throttle response. This predictability is not just a matter of preference but also enhances the driver’s control and connection with the vehicle, especially in high-performance driving situations.
Sound
The sound of a naturally aspirated engine is often described as more authentic and visceral compared to forced induction engines. The direct, unadulterated engine note is a significant factor for many car enthusiasts. In high-end sports cars, the engine sound is crucial to the driving experience. Naturally, aspirated engines deliver a pure, undistorted roar that is music to the ears of many.
Advantages of Naturally Aspirated Engines
The preference for naturally aspirated engines stems from their simplicity, reliability, linear power delivery, and distinctive sound. While they may not offer the same power density or fuel efficiency as forced induction engines, their advantages make them a favored choice for many driving enthusiasts and in applications where reliability and ease of maintenance are paramount.
Consistent Performance
Naturally, aspirated engines provide consistent performance without turbo or supercharger systems’ complexities and potential lag. This consistency is particularly advantageous in driving situations that demand precise throttle control, such as track racing or spirited driving on winding roads.
Durability
The more straightforward mechanics of naturally aspirated engines often mean less wear and tear over time. Without the high pressures and temperatures associated with turbocharging or supercharging, these engines can have a longer lifespan, assuming proper maintenance.
Maintenance
Maintenance on naturally aspirated engines is often more accessible and less costly, with fewer components and less complexity. This accessibility is particularly valued by those who prefer to maintain their vehicles themselves.
Disadvantages of naturally aspirated engines

Power Density
Naturally, aspirated engines typically have a lower power output than their turbocharged or supercharged counterparts of the same size. This limitation is due to their reliance on atmospheric pressure, which restricts the amount of air drawn into the combustion chamber.
Fuel Efficiency
Generally, naturally, aspirated engines are less fuel-efficient, especially in higher-performance models. This is partly because these engines must be more significant to produce the same power as a smaller, forced induction engine, increasing fuel consumption.
History of Lamborghini and Naturally Aspirated Engines

Lamborghini’s Dedication to Naturally Aspirated Power
Lamborghini’s reputation in the high-performance sports car realm is deeply intertwined with its commitment to naturally aspirated engines. This dedication underscores the brand’s focus on delivering a raw and visceral driving experience, marked by aggressive power delivery and an unmistakable engine roar.
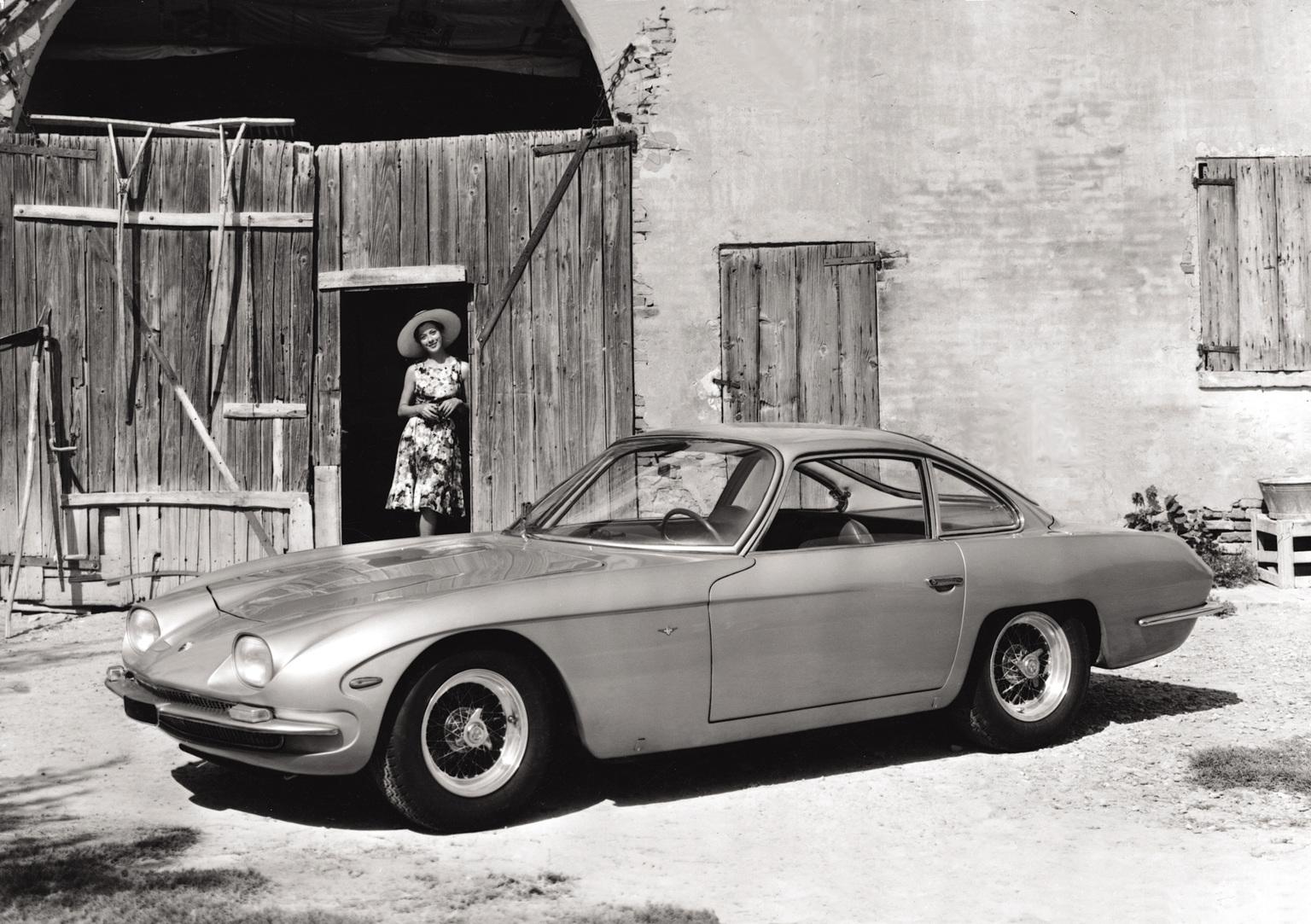
The First Lamborghini with a Naturally Aspirated Engine
Lamborghini 350 GT (1964): Lamborghini’s foray into high-performance automotive engineering began with the 350 GT. It was powered by a 3.5L V12 engine designed by Giotto Bizzarrini, delivering 280 hp and achieving a top speed of 254 km/h, setting a high engine performance and reliability benchmark.
Historic Naturally Aspirated Models
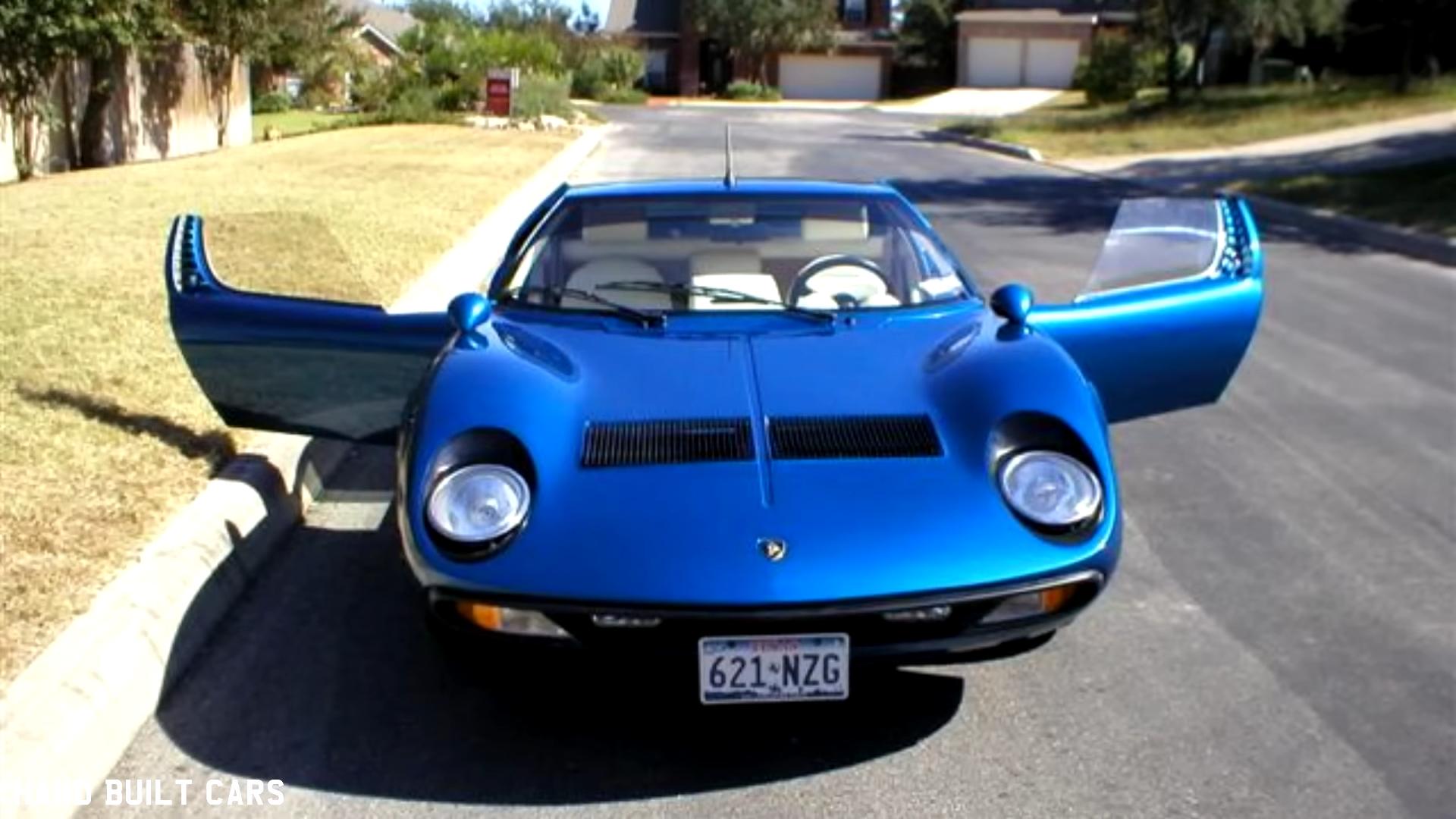

- Miura (1966-1973): The Miura, a game-changer with its mid-mounted 3.9L V12 engine, initially produced 350 hp, later upgraded to 380 hp in the Miura S and 385 hp in the Miura SV. It’s credited with pioneering the mid-engine layout in sports cars.
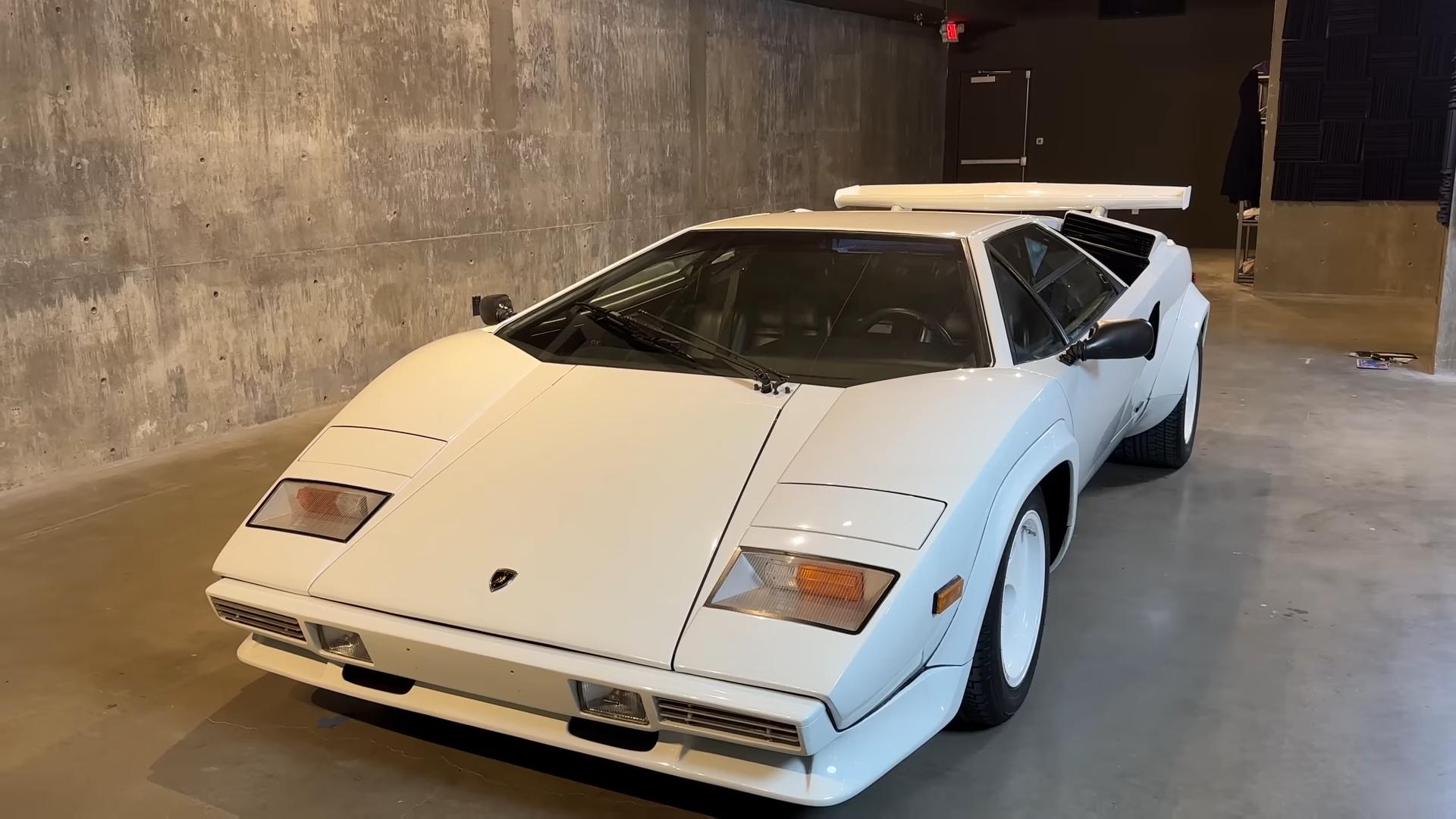

- Countach (1974-1990): The Countach, famous for its striking design and powerful engine, started with a 4.0L V12 engine (375 hp) and evolved to a 5.2L V12 (455 hp in the 25th Anniversary Edition), showcasing Lamborghini’s progressive engineering feats.
Current Models with Naturally Aspirated Engines
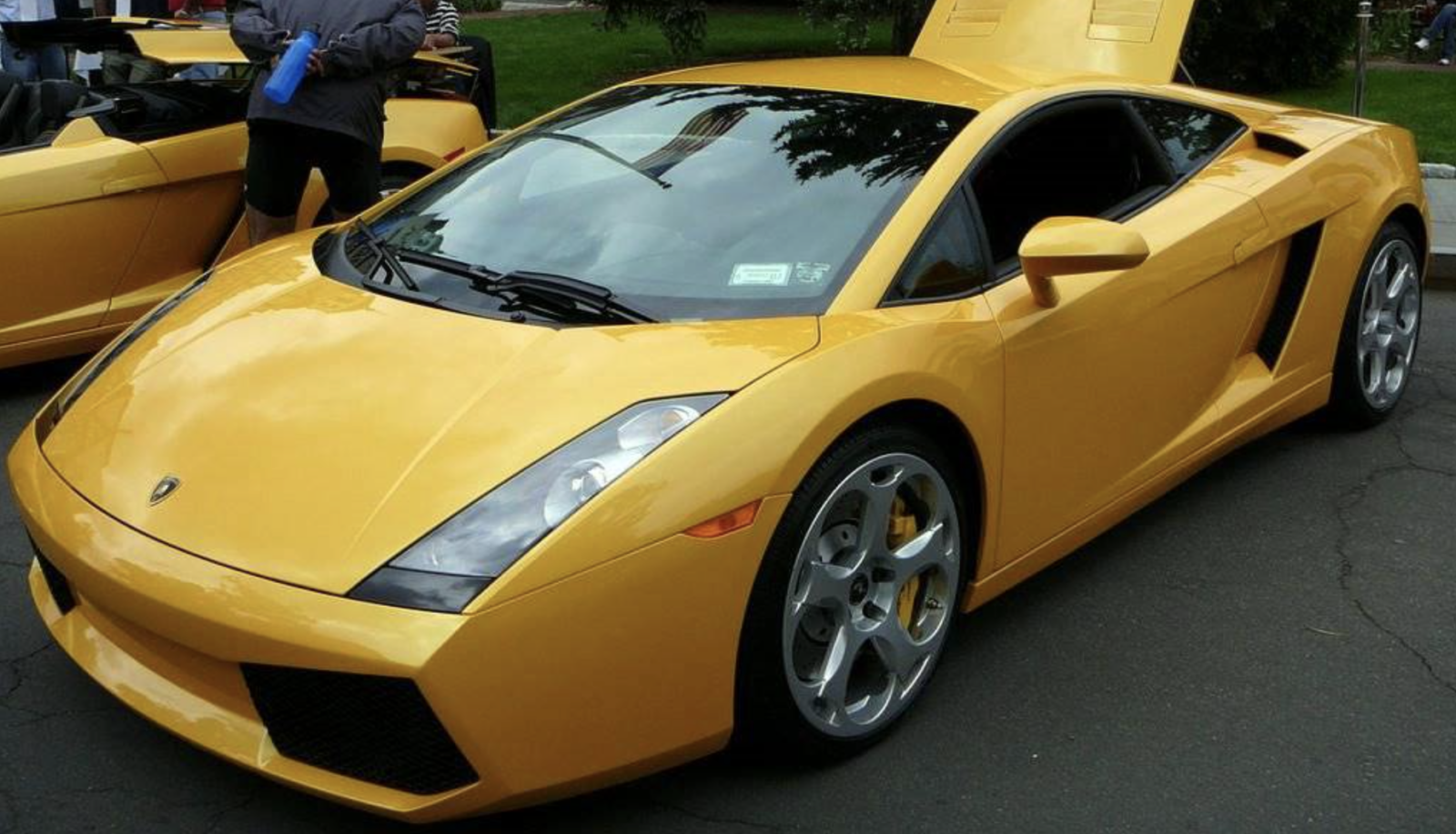

- Gallardo (2003-2013): The Gallardo, one of Lamborghini’s best-selling models, was pivotal in shaping the brand’s modern era. Equipped with a 5.0L V10 engine upon its initial release, it could produce 500 horsepower. This engine was updated in later versions like the Gallardo LP 560-4, which featured a 5.2L V10 engine delivering 560 hp. Known for its more approachable size and dynamic performance, the Gallardo played a crucial role in making the Lamborghini brand more accessible to a broader audience. Its engine’s thrilling sound and reliable performance exemplified Lamborghini’s naturally aspirated engine prowess.
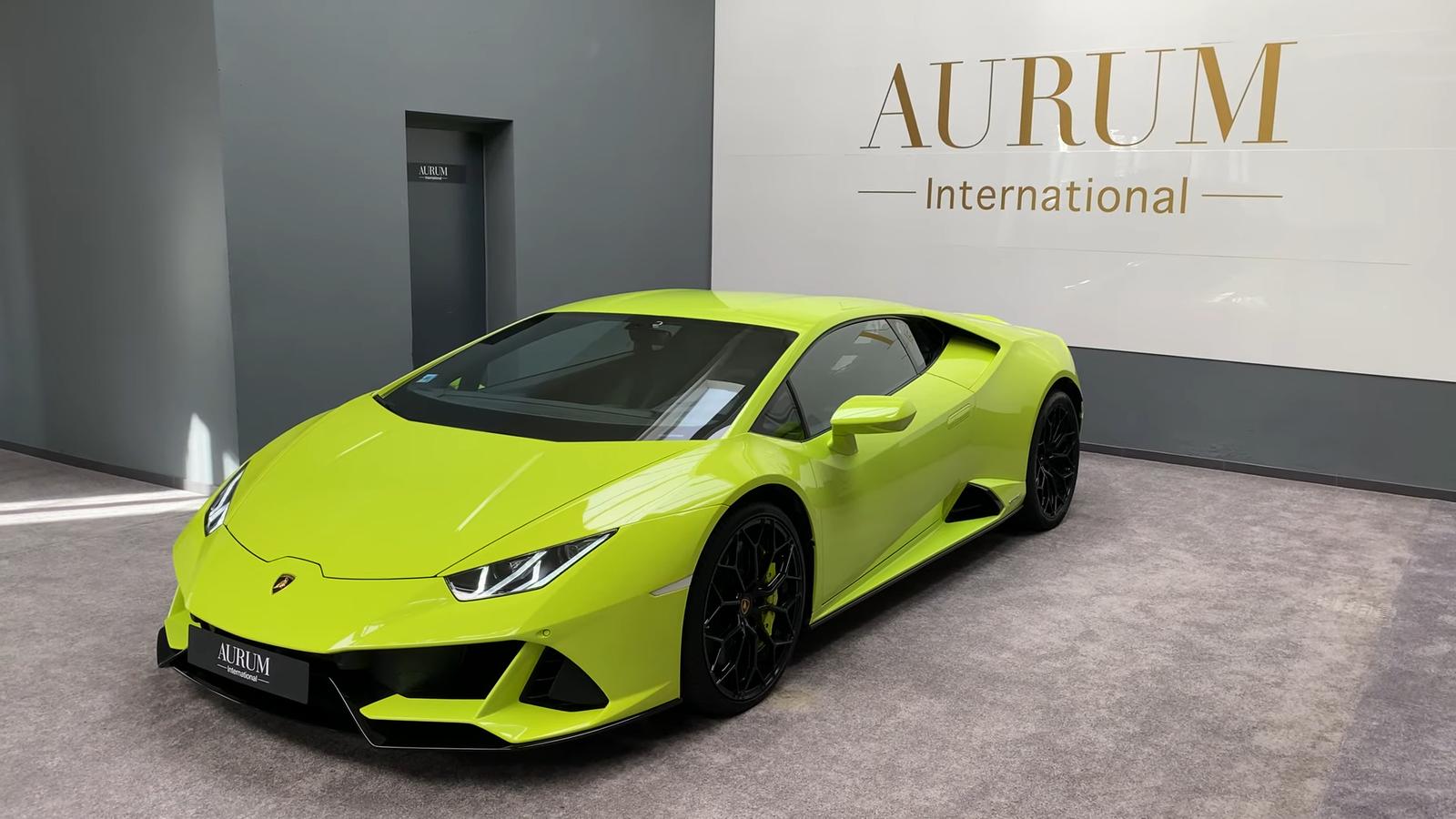

- Huracán (2014-Present): The Huracán, powered by a 5.2L V10 engine, offers varying power outputs from 580 hp (RWD version) to 631 hp (Performante and EVO models). It’s acclaimed for its responsive, high-revving engine and dramatic sound.
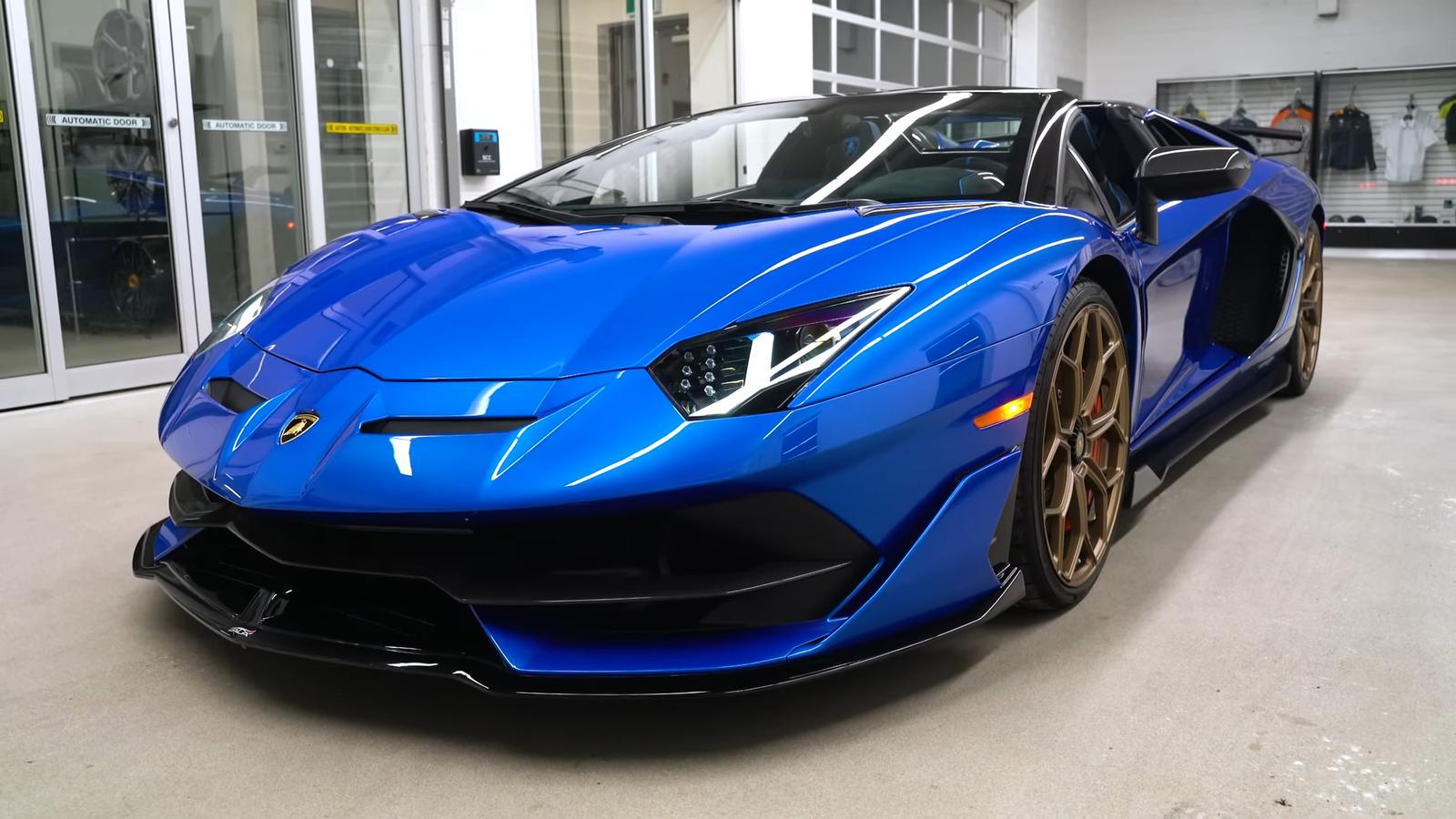

- Aventador (2011-2023): Lamborghini’s flagship, the Aventador, features a 6.5L V12 engine, evolving from 690 hp in the original model to 759 hp in the SVJ variant. The Aventador SVJ accelerates from 0-100 km/h in just 2.8 seconds, showcasing top-tier performance.
Lamborghini’s storied history with naturally aspirated engines, from the 350 GT to the Gallardo and the current line-up of the Huracán and Aventador, reflects a relentless pursuit of automotive excellence. These engines are more than just power sources; they are the soul of Lamborghini cars, providing an unparalleled symphony of sounds and an engaging driving experience that resonates with enthusiasts worldwide. As the automotive landscape evolves, Lamborghini’s naturally aspirated engines are monuments to the era of pure, unassisted power and emotion.